How does lignin’s role as a natural binder enhance the durability, energy efficiency, and overall performance of biomass pellets in industries such as power plants, boilers, and others?
Biomass pellets and their applications across various industries such as Power Plants, Boilers, Dairy, Pharmaceutical, and Namkeen Industries. PelletIndia.com offers turnkey plant solutions based on the type of biomass available in the region, using advanced machinery to ensure efficient pellet production.
Lignin is often referred to as a “natural binder” or even a “gift of nature” for biomass pellet production because of its crucial role in binding biomass fibres together during pelletization. This not only improves the structural integrity of the pellets but also enhances their energy properties. Here’s how lignin contributes to producing pellets with proper Gross Calorific Value (GCV) and other benefits:
Key Roles of Lignin in Pellet Production:
- Natural Binder: Lignin acts as a natural adhesive during the pelletizing process. When biomass is compressed at high temperatures in a pellet mill, lignin softens and binds the particles together, eliminating the need for artificial binders. This natural binding ability gives pellets their durability and solid structure.
- Enhancing Durability: Lignin improves the mechanical strength of pellets, making them more resistant to wear and tear during transport, handling, and storage. A higher lignin content results in pellets that can withstand higher pressures without crumbling.
- Boosting GCV: Since lignin is an organic polymer with a relatively high carbon content, it contributes significantly to the Gross Calorific Value (GCV) of biomass pellets. The energy density of the pellets increases as the lignin content rises. For example:
- Softwood pellets, which have a higher lignin content (~27%), tend to have a GCV of around 4300-4500 kcal/kg.
- Hardwood pellets with lignin around 23% offer a similar or slightly lower GCV but remain highly efficient for combustion.
- Water Repellent Properties: Lignin also has water-repelling properties, making the pellets more resistant to moisture absorption. This characteristic is essential for storage, as it prevents degradation and energy loss in humid environments.
- Contribution to Combustion Efficiency: During combustion, lignin helps ensure steady and efficient burning, reducing the production of fine dust and ensuring a higher calorific output. Pellets with higher lignin content tend to burn more cleanly and produce less ash.
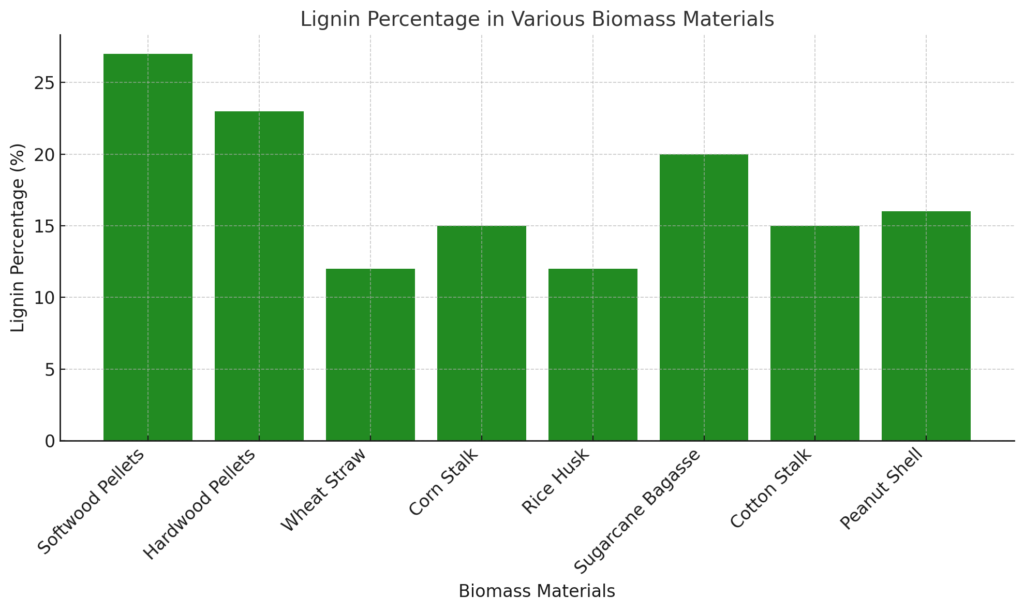
Biomass Materials with High Lignin Content:
- Wood Pellets (Softwood): High lignin content results in better pellet durability and high GCV.
- Sugarcane Bagasse: Lignin, along with fibre, gives bagasse pellets a good energy output and durability, making it a suitable material for biomass energy production.
- Cotton Stalk & Peanut Shell: Moderate lignin content enables the formation of durable pellets, but additional processing might be required for uniformity in GCV.
Benefits for Industries:
Industries like power plants, boilers, and others that rely on biomass pellets benefit from higher lignin content because it ensures consistent energy output, cleaner combustion, and lower operational costs associated with handling and storage.
In essence, lignin is not just a natural binder but also a vital contributor to producing high-quality, energy-dense pellets that offer better efficiency, durability, and sustainability in various applications.
For more details regarding Biomass Plant Machinery, please contact us without hesitation:
Contact:
- Phone: +919427210483
- Email: [email protected]
- Website: www.PelletIndia.com
